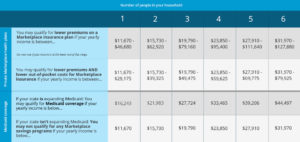
It’s been five years since Congress passed health care reform, but many people are still missing out on possible savings, like lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs, just because they don’t know about them. The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (www.cms.gov) and www.healthcare.gov are two websites that can provide detailed information on how you can save on health insurance. The chart below can be used as a general guide.
Are you thinking about getting coverage, but finding yourself overwhelmed by all your options? Visit the Working America Health Care (WorkingAmericaHealthCare.org/AFM) website, or call 1-855-589-4253, to get personalized, unbiased support before, during, and after plan enrollment. As a member of the AFM, you can have a complimentary personal health advocate answer questions about coverage, help you understand your benefits, recommend doctors, help negotiate medical bills, and much more.
Health Insurance Lingo
When people try to explain how the Marketplace health insurance under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) works, it may sound like a foreign language. Here is a glossary of some key health insurance words to help you better understand the jargon:
Network: the facilities, providers, and suppliers your health insurer has contracted with to provide health care services. Through your insurance provider you should be able to find out which providers are “in-network,” sometimes called “preferred-providers” or “participating providers.” It may be more expensive to see an “out-of-network” provider. (These networks do change, so check with your provider each time you make an appointment to find out how much you will need to pay.)
Deductible: the amount you owe for health care services your health insurance or plan covers before your health insurance or plan begins to pay. For example, if your deductible is $1,000, your plan won’t pay anything until you’ve met your $1,000 deductible for covered health care services, subject to the deductible. The deductible may not apply to all services.
Co-insurance: your share of the costs of a covered health care service, calculated as a percentage of the allowed amount for the service. You pay co-insurance, plus any deductibles you owe. For example, if the health insurance plan’s allowed amount for an office visit is $100, you’ve met your deductible, and your co-insurance payment is 20%, you would pay $20. The health insurance or plan pays the rest of the allowed amount.
Co-payment or co-pay: an amount you may be required to pay as your share of the cost for a medical service or supply, like a doctor’s visit, hospital outpatient visit, or prescription drug. A co-payment is usually a set amount, rather than a percentage. For example, you might pay $10 towards a doctor’s visit, lab work, or prescription.
Premium: the amount that must be paid for your health insurance or plan. It is paid monthly, quarterly, or yearly, and is separate from your deductible, your co-payment, or your co-insurance. If you don’t pay your premium, you may lose your coverage.
Out-of-pocket maximum: the most you pay during a policy period (usually one year) before your health insurance or plan pays 100% for covered essential health benefits. This limit includes deductibles, co-insurance, co-payments, or similar charges, and any other expenditure for a qualified medical expense. This limit does not include premiums or spending for nonessential health benefits.
Explanation of benefits (or EOB): a summary of health care charges that your health plan sends you after you see a provider or get a service. It is a record of the health care you, or individuals covered on your policy, received and how much your provider is charging your health plan. If you have to pay more for your care, your provider will send you a separate bill.
Health Insurance Checklist
With more than 10,000 options through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplaces, it’s critical to know what you want from your health insurance to get the most value for your family. Here’s a list of items you will want to consider.
- Does the plan provide coverage for pre-existing conditions, maternity care, mental health services, prescription drugs, and dental and vision care?
- Does the plan have long waiting periods?
- Does the plan provide other support and wellness services for its members?
- How much will the plan cost each year, including the premium, deductible, co-payments and/or co-insurance, and out-of-pocket maximum? What is the lifetime limit on coverage?
- How large is the plan’s network and how close are you to the plan’s doctors and hospitals?
- Does the plan have a clear arrangement for specialist referrals?
- How does the plan’s disputed claims appeal process work?
Even if you’re already insured, it’s still a good idea to shop around with the Working America Health Care program.